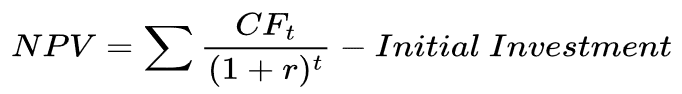CFA Level 1
CFA Level 1
Corporate Issuers - Exam Ready Notes
1. Organizational Forms, Corporate Issuer Features, and Ownership
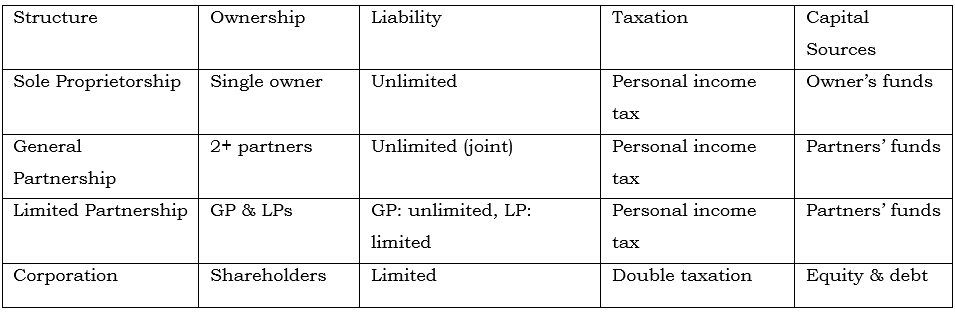
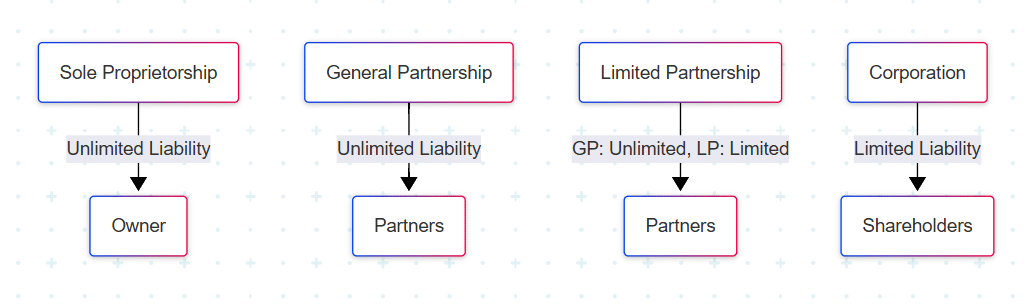
Public vs. Private Companies
- Public: Shares traded on stock exchange, subject to regulatory disclosure, can raise large amounts of capital.
- Private: Fewer shareholders, less regulatory burden, limited access to capital markets.
Lifecycle Stages:
- Startup → Growth → Maturity → Decline
2. Investors and Other Stakeholders
Stakeholder Groups
- Lenders: Provide debt, seek interest/principal, priority in claims.
- Shareholders: Provide equity, seek dividends/capital gains, residual claim.
- Employees: Seek job security, compensation, benefits.
- Suppliers/Customers: Seek stable relationships, product quality, timely payments.
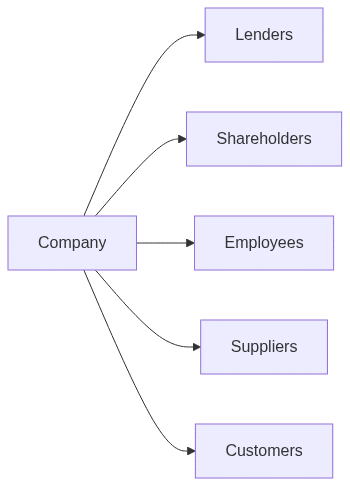
Stakeholder Map
ESG Considerations
- Environmental: Resource use, pollution, climate impact.
- Social: Employee relations, diversity, community impact.
- Governance: Board structure, executive compensation, shareholder rights.
3. Corporate Governance: Conflicts, Mechanisms, Risks, and Benefits
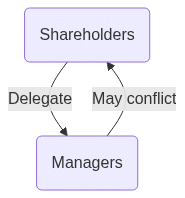
Principal-Agent Conflicts
- Managers (Agents) may pursue personal goals over shareholder interests.
- Mechanisms to Align Interests:
- Board oversight
- Executive compensation linked to performance
- Shareholder voting rights
Agency Conflict
Risks and Benefits
- Risks: Fraud, mismanagement, value destruction.
- Benefits: Efficient capital allocation, risk management, value creation.
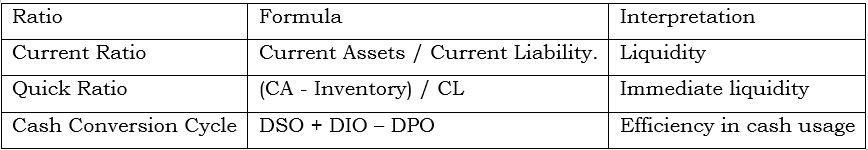
4. Working Capital and Liquidity
Key Ratios

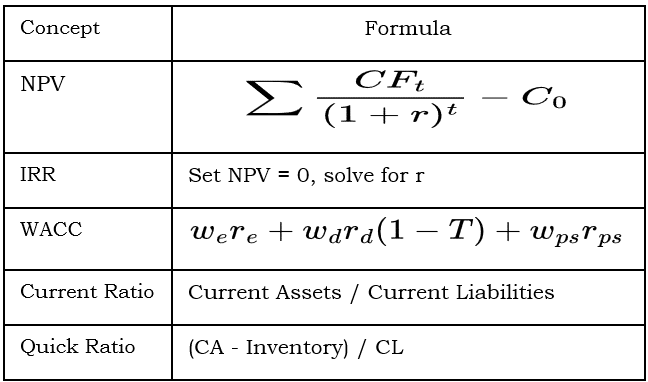
5. Capital Investments and Capital Allocation
Capital Budgeting Techniques
- Net Present Value (NPV):
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR):
Discount rate that makes NPV = 0.
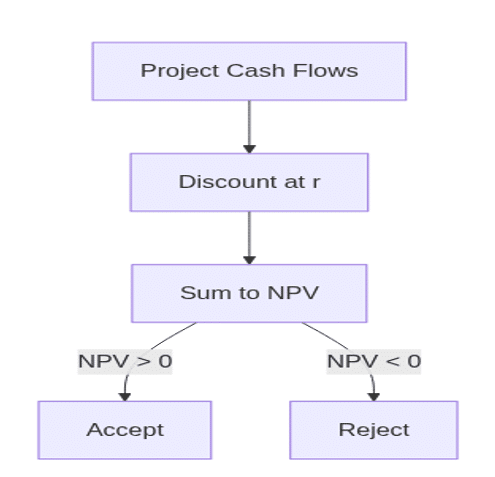
NPV vs. IRR Decision
Capital Allocation Pitfalls
- Over-optimism in forecasts
- Ignoring risk
- Poor post-investment review
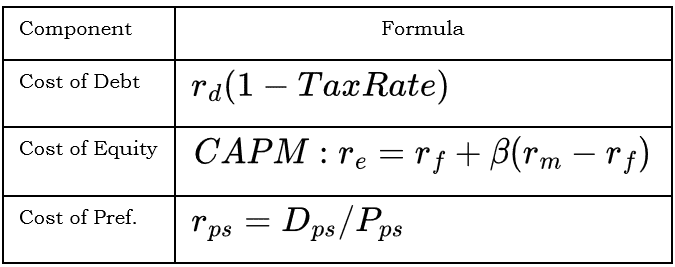
6. Capital Structure
Cost of Capital Components

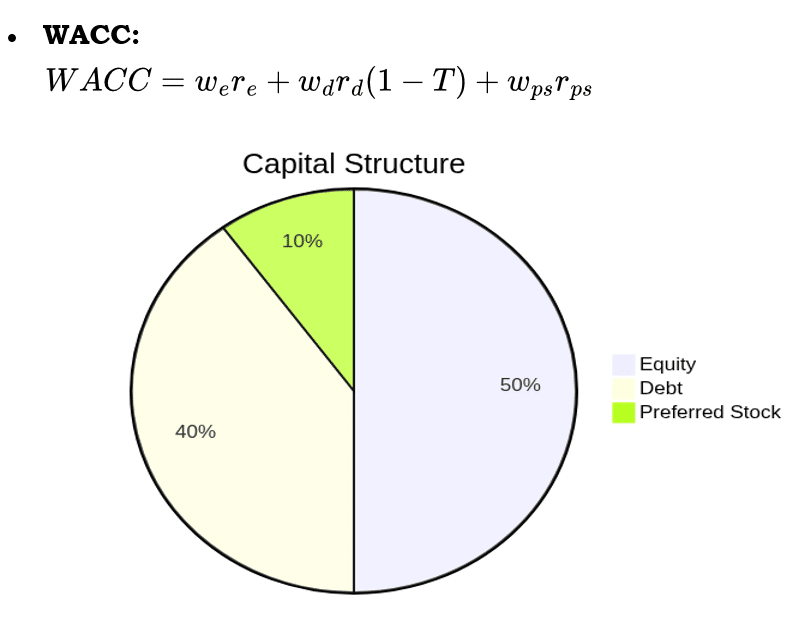
Capital Structure Pie Chart
Theories
- Modigliani–Miller: Capital structure irrelevant in perfect markets.
- Pecking Order: Firms prefer internal financing > debt > equity.
- Trade-off Theory: Balance tax shield of debt vs. bankruptcy risk.
7. Business Models
Types
- Product-based: Sell goods (e.g., manufacturing)
- Service-based: Sell services (e.g., consulting)
- Platform: Connect buyers and sellers (e.g., e-commerce)
- Subscription: Recurring revenue (e.g., SaaS)
Business Model Canvas (Simplified)
Tips:
- Focus on understanding the rationale behind formulas and corporate decisions, not just memorization.
- Practice interpreting ratios and capital budgeting results in real scenarios.
- Use diagrams to visualize business relationships and flows.
Transform your career with our Investment Banking course in India and secure your dream job as an investment banker!