CFA Level 1
CFA Level 1
Alternative Investment - Exam Ready Notes
CFA Level 1 Alternative Investments – Summary Notes
1. What Are Alternative Investments?
Definition:
Assets outside traditional stocks, bonds, and cash.
Categories:
- Private Capital: Private equity, private debt
- Real Assets: Real estate, infrastructure, natural resources
- Hedge Funds
- Digital Assets: Cryptocurrencies, tokens, NFTs, etc.
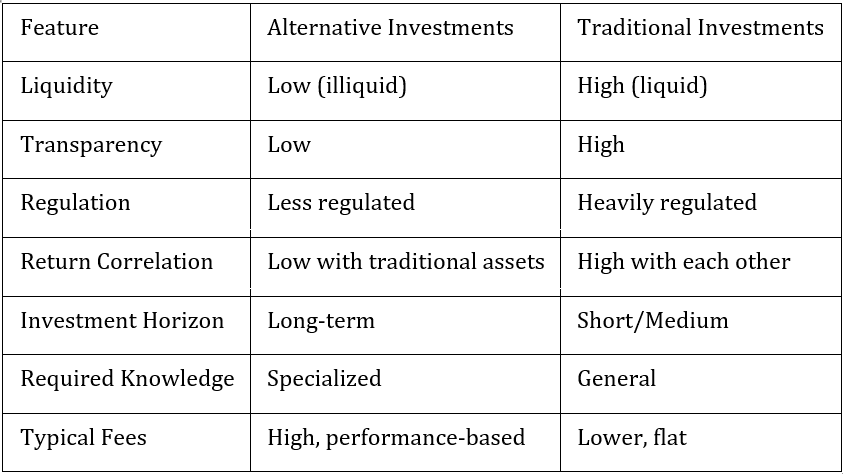
Key Features Table
2. Why Invest in Alternatives?
- Diversification: Low correlation with traditional assets (see correlation matrix below)
- Potential for Higher Returns: Often compensate for illiquidity and complexity
- Inflation Protection: Especially real assets and commodities
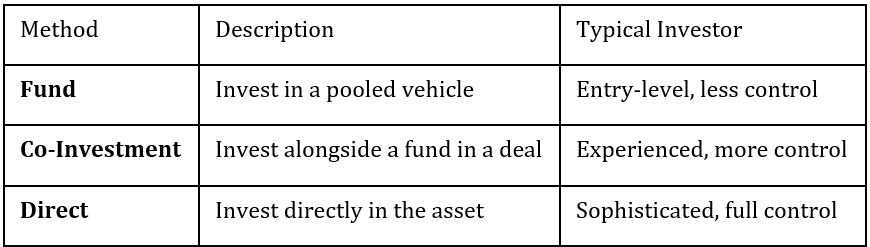
3. Investment Methods
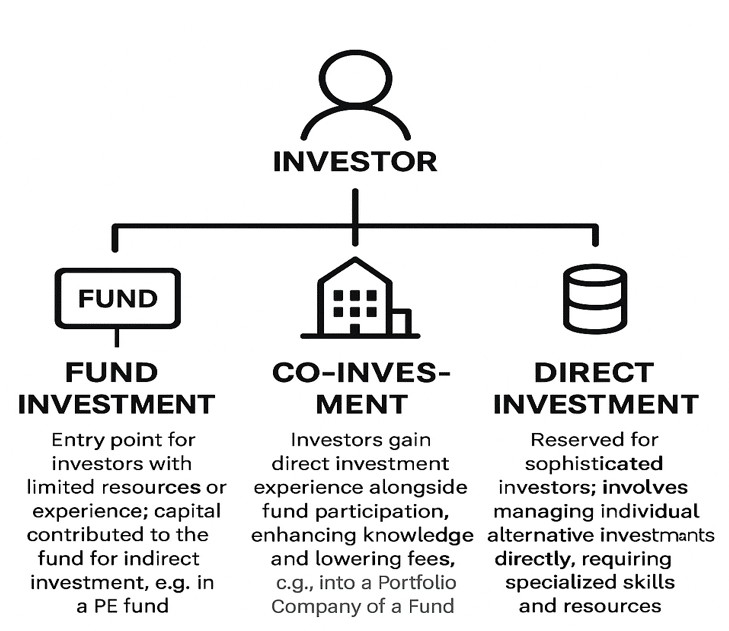
Investment Methods
4. Structures & Compensation
Limited Partnerships (LP/GP):
- GP (General Partner): Manages, unlimited liability, earns management + performance fees
- LP (Limited Partner): Passive investor, limited liability
Fee Structure:
- Management Fee: % of committed capital or AUM (1–2%)
- Performance Fee (Carry): % of profits above hurdle (often 20%)
- Hurdle Rate: Minimum return before carry applies
- High-Water Mark: No performance fee unless NAV exceeds prior peak
- Clawback: LPs can reclaim excess performance fees if later losses occur
5. Private Capital
Private Equity
- Venture Capital: Early-stage, high-growth firms
- Buyouts: Mature firms, often with leverage
- Distressed/Turnaround: Struggling firms, restructuring
Key Concepts:
- Exit Strategies: IPO, trade sale, secondary sale, recapitalization, write-off
- Valuation: Comparable companies, precedent transactions, DCF
Private Debt
- Direct Lending: Loans to mid-market companies
- Mezzanine Debt: Subordinated, often with equity kicker
- Distressed Debt: Buying at discount, aiming for restructuring gains
6. Real Assets
Real Estate
- Types: Residential, commercial, industrial, REITs
- Returns: Rental income, capital appreciation
- Valuation: Sales comparison, income approach, cost approach
Infrastructure
- Types: Economic (roads, airports), Social (schools, hospitals)
- Features: Long life, inflation-linked cash flows, public-private partnerships
Natural Resources
- Types: Commodities, farmland, timberland
- Returns: Price appreciation, yield (e.g., crops, timber harvest)
7. Hedge Funds
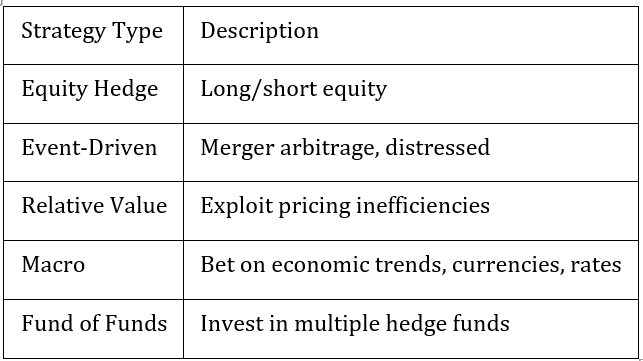
· Fee Structure: “2 and 20” (2% management, 20% performance)
· Liquidity: Lock-ups, gates, notice periods
8. Digital Assets
- Types: Cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum), tokens, NFTs, stablecoins
- DLT/Blockchain: Distributed ledger, consensus mechanisms (Proof of Work, Proof of Stake)
- Risks: High volatility, regulatory uncertainty, custody/security
9. Performance & Returns
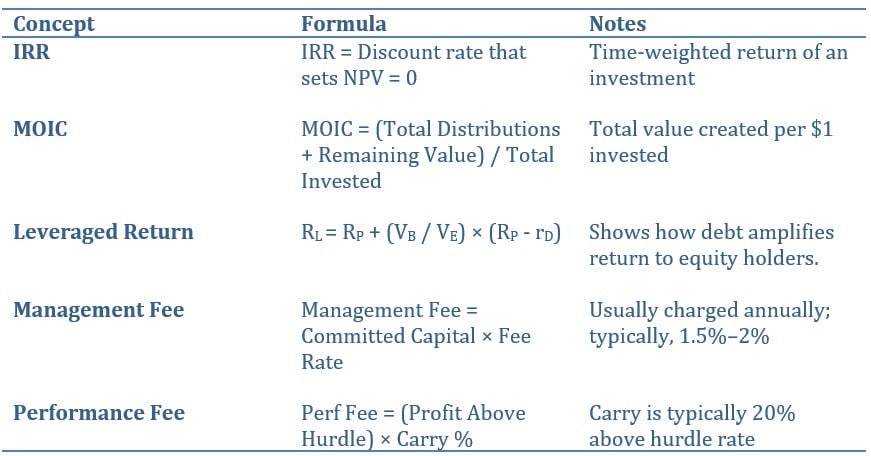
- Return Calculation: Often IRR (Internal Rate of Return) due to irregular cash flows
- MOIC (Multiple on Invested Capital): (Total value returned + remaining value) / total invested
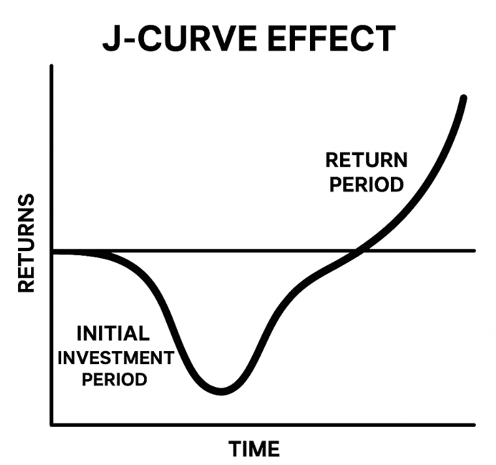
- J-Curve Effect: Initial negative returns (fees, investments), positive returns later
J-Curve Graph (for Word):
- X-axis: Time, Y-axis: Cumulative Return
- Curve dips below zero, then rises above
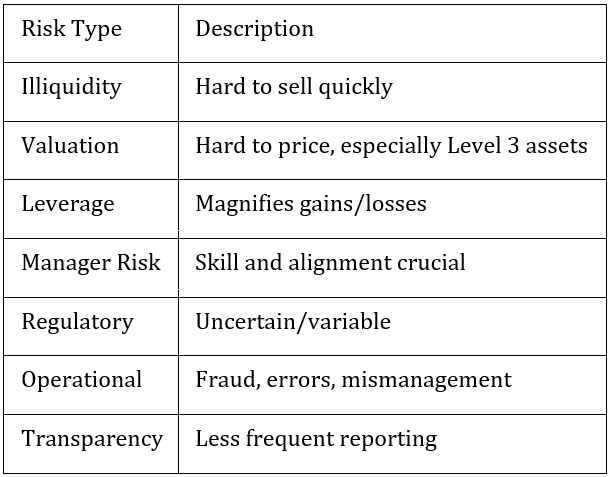
10. Risks in Alternatives
11. Due Diligence
- Assess manager skill, experience, and track record
- Review fund terms, lockups, redemption policies
- Analyze underlying asset risks, valuation methods
12. Key Formulas
Transform your career with our Investment Banking course in India and secure your dream job as an investment banker!